[Update 1] Louvain-Performance: Weights of Nonexistent Edges
Earlier, I wrote a post on how performance on weighted graphs uses a meaningful maximum M to account for the weights of nonexistent edges. At that time, my challenges were (1) figuring out how to calculate M, and (2) changing my…
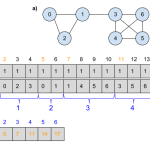
Creating the Adjacency Matrix
We are now able to construct an adjacency matrix of the network. As Anastasia explained in a previous post, we will use the adjacency matrix in silhouette index to find the shortest path between all pairs of vertices. Our matrix…
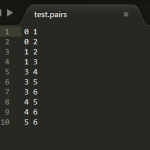
Input/Output Issue
The input file represents the network. It should be formatted as a space-delimited file, where each line contains the start node, destination node, and an optional edge weight. The test network. It is undirected and unweighted. The input file for…
Louvain-Performance: Weights of Nonexistent Edges
One of the tricky things about calculating performance is that it factors in nonexistent edges between vertices in different communities. The more of these edges exist, the higher the overall performance score, because they count as correctly-interpreted edges. That is, since the two…
Switch to Java
We recently switched from the C++ to the Java implementation of the Louvain method. Our main concern with the C++ implementation was how it handled serialization. With C++, we had to deal with the serialized version of the network to…

Code Implementation
Today, Christina, Jennifer, and I met to work together on implementing the metrics in the Louvain algorithm. Jennifer and I worked on the silhouette index. We began by discussing the psuedo code that I wrote up recently and identifying the…
10/26/15 Meeting
In today’s meeting, we went over our progress over the last couple weeks: Those of us who did not know C++ before this semester have now learned the language. We have all studied and understood our individual metrics (Anastasia – silhouette;…
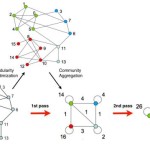
Louvain Algorithm
At our meeting on 09/18/15, I presented the Louvain Algorithm as outlined in the paper “Fast unfolding of communities in large networks”. This method centers around optimizing modularity, which measures the density of the links inside of the communities as…
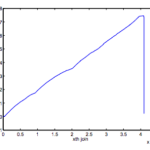
CNM Algorithm
At our meeting on 09/18/15, we discussed the two algorithms (Louvain and CNM) that we’ll be investigating this year. I presented on the CNM algorithm, as described in Clauset, Newman, and Moore’s paper “Finding community structure in very large networks.” Just…
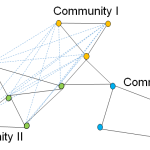
Quality Metrics
Community quality metrics are measurements of how well communities are formed. Good metric values generally reflect networks where connections are denser within communities than between communities. We are getting ready to implement various quality metrics in the Louvain method, an…